
As we continue to cast an eye on the MSP of the future, the topic of cybersecurity, in all its twists, turns, and frustrations, cannot be ignored. What might have been a minor part of an MSP’s portfolio previously is rapidly evolving as mission critical to both continued competitiveness and legitimacy of the business. Bottom line? No customer engagement around technology and business solutions should occur without a dose of cybersecurity acumen included.
Consider just a few stark statistics from CompTIA’s 2021 State of Cybersecurity report:
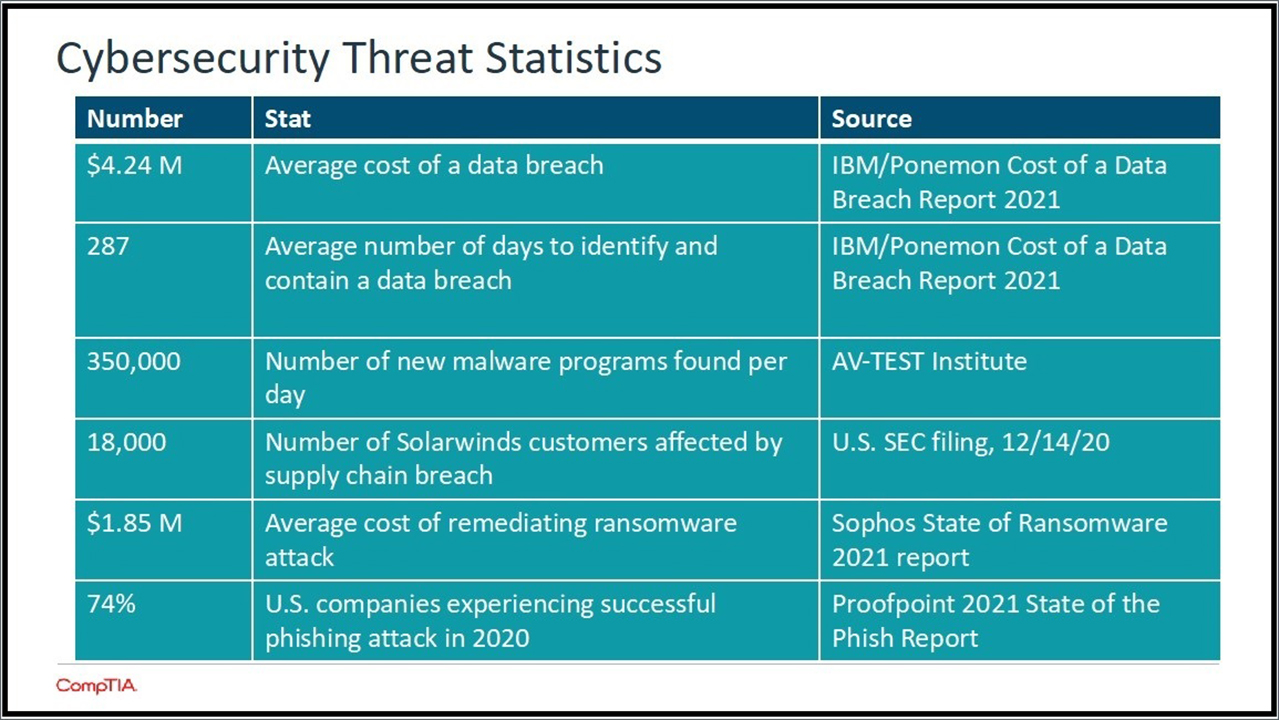
surgInto this morass steps the MSP, steward of its customer’s technology environment. In year’s past, cybersecurity has mainly existed as a basic set of product offerings from MSPs; think antivirus and firewall software. And many MSPs would admit freely that they were behind the eight ball, or at least somewhat overwhelmed, by the need to step up to more sophisticated cybersecurity techniques and services.
Access the Trends in Managed Services 2022: The Impact of Cybersecurity infographic now!
Cybersecurity: MSPs Step into the Fray
Yet today many MSPs are waking up. A year ago, MSPs cited the need for updated cybersecurity expertise as the No. 1 driver for success in the next two years. Flash forward to today, and more than half (54%) continue that line of thinking, saying that deep skills and specialization in cybersecurity (penetration testing, ransomware protection, cyber insurance and compliance offerings, to name a few) are a major factor necessary to their success as a business. That leaves 4 in 10 MSPs, however, that continue to believe offering cybersecurity at the more basic level is enough to have a moderate impact on their success. A small portion (5%) of MSPs, many of them with fewer than 10 employees of their own, relegate cybersecurity to a minor role in their company’s prospects.
.jpg?sfvrsn=9b0d6170_2)
In general, whether pure play or hybrid, MSPs report improvement to their cybersecurity skill sets and a broadening of their offerings in the last 12 months. That’s good news. In 2021, 28% of MSPs acknowledged either being behind their cybersecurity goals targets altogether or still in the early experimental stages with cybersecurity services. That number dropped by half in 2022 to 14%. And of those that had either reached their cybersecurity goals in 2021 or were on target to do so over the next two years, progress continued in 2022. While two thirds of MSPs fell into one of those categories in 2021, 85% did so this year.
The surge in focus and advancement in cybersecurity is paying off in terms of revenue for many MSPs. As a percentage of total revenue, cybersecurity accounts for a healthy 10%-50% of sales for the majority of MSPs (77%). But what’s even more interesting is the percentage of MSPs that say cybersecurity dollars will make up more than half of their total revenue in two years’ time. That group doubled to 16% from the 8% of MSPs who say they are achieving that amount today.
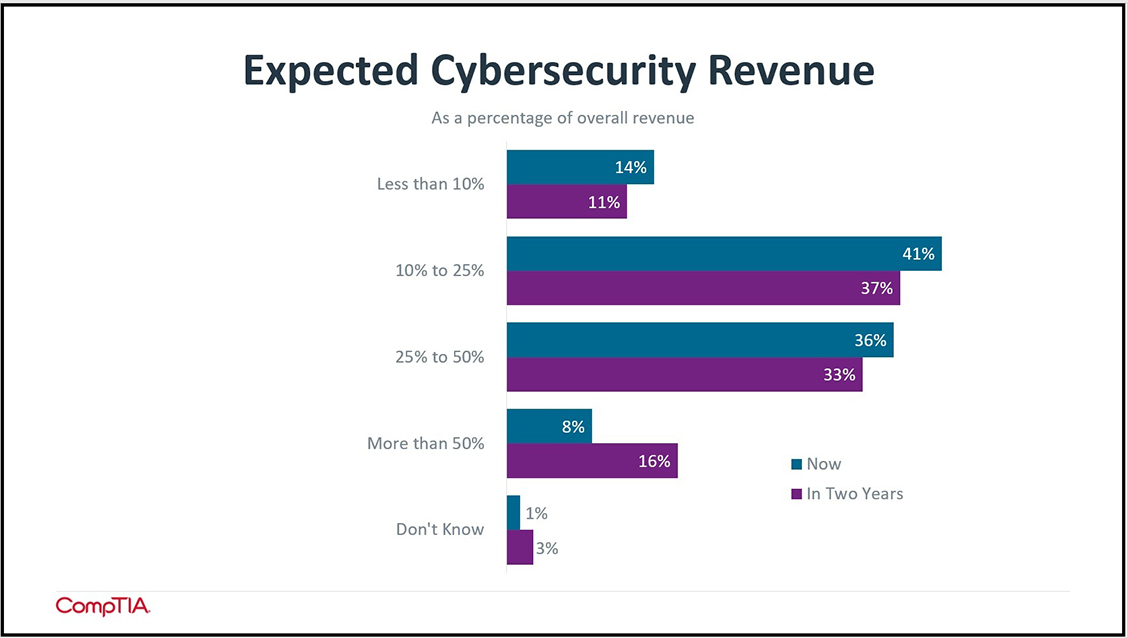
These positive revenue gains did not—and will not—arrive without actions being taken. It seems that despite the ongoing pandemic that has tempered investment for many companies both in and out of the channel, MSPs in the past couple of years have embarked down a variety of paths to gain more cybersecurity proficiency and pad their portfolios.
The actions fall into two categories: those pertaining to internal staff/human resources and those involving in partnering.
The percentages are fairly balanced across the three human resources-related actions. Forty-two percent of MSPs said they hired personnel with specific cybersecurity skill sets in the last year. Those skills could range from expertise in data, endpoint, applications, and network security to acumen in identity management, data analysis, penetration testing, and/or cryptography (among others). Other areas to beef up through targeted hiring included finding new workers that understand today’s regulatory and compliance landscape or are adept at training a customers’ user population on cybersecurity best practices. A similar percentage of MSPs (41%) looked inward, retraining their existing workforce to update their cybersecurity skills. Another 36% paid for their employees to attain cybersecurity-related professional certifications.
On the partnering side, a surprising number of MSPs looked for help from other MSPs. Forty-four percent said they partnered with peers, chiefly MSSPs, to fill in cybersecurity skills gaps. Presumably, this is a quid pro quo-type arrangement in which other skills are offered in return to fill in gaps the MSSP in question is lacking. If done right (formalized contracts, accountability spelled out, etc.), these types of partnerships are a quick way to meet customer demand on the fly and establish a “bigger” presence in the marketplace.
Finally, on the partnership side, 36% of respondents increased engagement with vendors or other security resources to stay on top of issues. That includes deciding to work with new cybersecurity vendors as well as boosting work with their existing vendors. Vendors in this space often have good intelligence into the threat landscape, a bonus for MSPs that cite keeping pace with the complexity and speed of cybersecurity attacks as a main challenge.

Getting Their Own House In Order
We’ve all seen the headlines: Solarwinds. Kaseya. Vulnerable MSPs as the malicious actor’s gateway to customer data. It goes on. In 2021, 62% of MSPs said they were very concerned about their own network being hacked to reach their customers’ assets; 30% were at least somewhat worried. Larger MSPs were understandably more fretful than the very smallest, given that they could provide access to a higher number of customers that were also more likely to be of a decent size themselves. But very few MSPs claimed no fear at all.
So, what have they done to mitigate the threats? Plenty, as it turns out. Like moves made to elevate their cybersecurity skills, MSPs have addressed their internal security posture issues with investments. The main steps they have taken include increasing their cybersecurity budget year over year; investing in the training and certification of their employees; partnering closely with their vendors; and for some, hiring a chief information security officer (CISO).
The results are heartening. In the 2022 study, the percentage of MSPs very concerned about hacking threats to their network declined to 38% from 62% the year before. It’s never smart to get too comfortable when it comes to cybersecurity, but this decrease in stress levels is presumably indicative of MSPs seeing results—good ones—from their redoubled efforts.
Want to learn more?
Check out Trends in Managed Services 2022
and Trends in Managed Services: The Impact of Cybersecurity.

 Add CompTIA to your favorite RSS reader
Add CompTIA to your favorite RSS reader

