Technology encompasses nearly every aspect of our lives, prompting a migration toward virtualization in the form of cloud computing. With this shift to cloud technologies IT pros are wondering which types of cloud services make sense for their organizations. If you’re asking WTF is the cloud and what are my options, keep reading for a breakdown of cloud types, cloud solutions and the basics you need to know to bring cloud computing to your organization.
Before you can implement a cloud solution, you need to determine which cloud type makes the most sense for your organization. What are the differences between the most common cloud types?
A public cloud solution utilizes services offered by a cloud service provider. In a public cloud architecture, a cloud service provider supplies the infrastructure, and various clients access the resources through multi-tenant hosting. This cloud solution allows clients to share hardware components, while dedicating memory, storage and other resources to the individual organizations.
The public cloud is advantageous because it is typically available at a lower cost. The main drawback is the security concerns of sharing hardware equipment with others. Public clouds are popular among smaller organizations that don’t have the capacity for internal manpower to manage dedicated hardware.

The private cloud is a cloud structure that allows you to set up your own private centralized data center. This infrastructure provides all the necessary computing components for geographically separated offices.
A private cloud solution offers the benefits of a centralized data center that is internally managed and controlled, but it is accessible by users in various locations. The drawback to a private cloud solution is the large expense of the necessary infrastructure and the staff needed to maintain and manage the data center.
Private clouds are ideal for organizations that operate in highly regulated industries, such as financial institutions or health care organizations.
Hybrid clouds are aptly named. This cloud solution is a marriage between public clouds and private clouds. With a hybrid cloud, organizations utilize the cost-effective resources of the public cloud, while maintaining some on-premises data centers.
The hybrid cloud allows organizations to take full advantage of the business benefits and cost savings of the public cloud, while keeping sensitive or regulated information secure on dedicated hardware. Hybrid clouds can be utilized by organizations of all sizes and are often selected for their flexibility.

This cloud architecture is similar to a public cloud because it allows for the sharing of resources. A community cloud is structured for multitenancy, but the structure specifically supports groups with similar needs, concerns or services. Community clouds can be provided by cloud service providers or might be started by a concerned organization.
A good example of a community cloud would be a group of health care providers acting to comply with HIPAA regulations.
Determining the type of cloud you need is a good first step. But before you can move to migration, you will need to ascertain your cloud service options.
Cloud services is an overarching term that refers to the different offerings available from selected providers. Cloud services range in price and complexity and are available from a variety of providers.
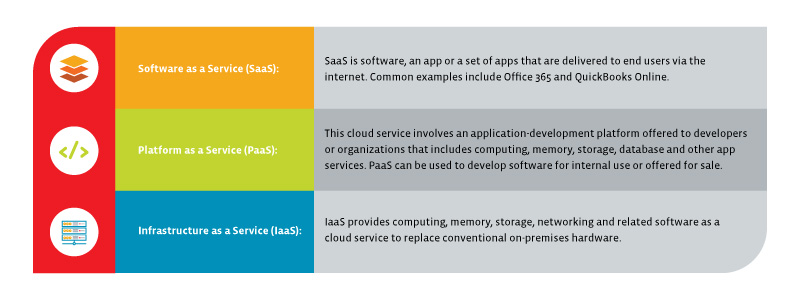
The following are examples of cloud services:
Other lesser-known cloud services include graphics as a service (GaaS), desktop as a service (DaaS) and disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), among others.
Before you can plan a cloud migration, it’s also important to understand cloud architecture and how it will affect your cloud computing needs.
Cloud solutions can be designed in three ways:
After determining a cloud structure, you need to decide which cloud service provider has what you need.

Businesses often seek to find the best cloud solution to fit their unique organizational needs. A large part of this decision is selecting a cloud service provider. There are four primary cloud service providers that control the majority of global cloud resources. However, there are other lesser known cloud solutions that offer specific services to niche markets.
The four most widely used cloud service providers all offer SaaS, PaaS, IaaS and many other cloud services on a global scale.
The major cloud service providers include:
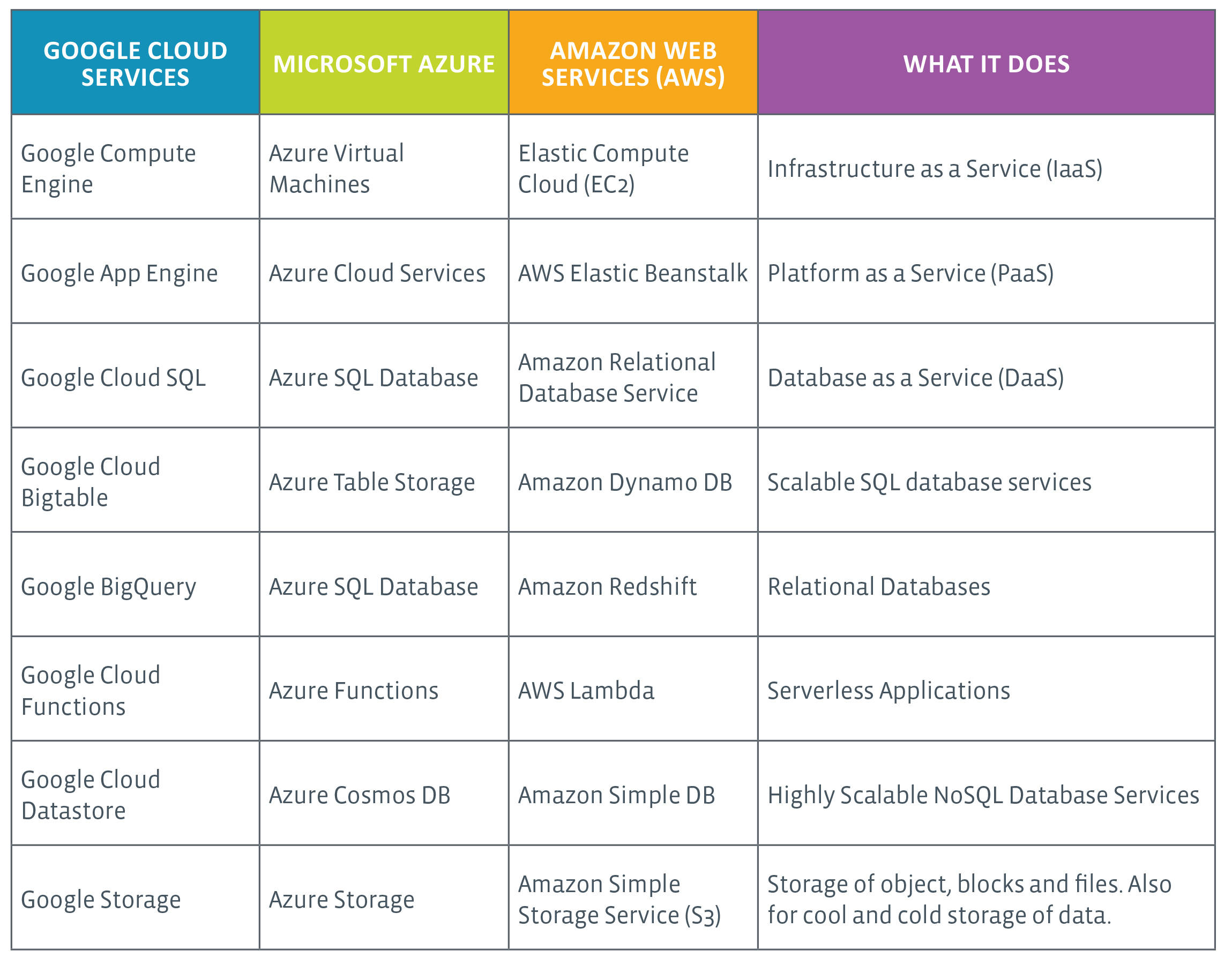
Learn more about the major cloud vendors.
Some other cloud solutions offering specific services include the following:
This is merely scratching the surface of the various cloud solutions that are available. However, these cloud service providers offer a solid base for understanding what kind of services are available.
No two businesses are the same. Before launching a cloud deployment, make sure you fully understand the options available to you and how different cloud solutions will impact your organization.
If you see yourself moving into a cloud job like cloud specialist, cloud engineer or even data center manager, check out CompTIA Cloud+ to make sure you have the skills employers are looking for. CompTIA Cloud+ validates the skills and abilities you need to implement and manage a successful cloud solution.

CompTIA Cloud+ is the only vendor-neutral, performance-based IT certification that views cloud computing as it relates to the broader ecosystem of IT operations.
This IT certification covers topics such as configuring and deploying cloud solutions and maintaining, managing and troubleshooting a secure cloud computing environment.
The Official CompTIA Cloud+ Study Guide and classes offered by CompTIA training partners can help you get the knowledge you need for a successful career in cloud computing. Download the CompTIA Cloud+ exam objectives to see what’s on the exam, and purchase the study guide to begin your training.