As cybersecurity threats evolve, our understanding of those threats must change—as should our knowledge of all the potential risks, and how to respond appropriately. To help tech companies accelerate their cyber resilience, CompTIA has launched the CompTIA Information Sharing and Analysis Organization (ISAO), an initiative that analyzes the latest cybersecurity threats and provides actionable threat intelligence to its members.
Membership in an ISAO helps protect our businesses, customers, and the tech industry. Members gain access to insight and information on the latest and biggest cyber risks as well as prescriptive, actionable steps to respond. But what exactly does joining an ISAO entail? Why is it important? And how can you benefit? We’ve got the answers to those questions—and more.
After reviewing the ISAO FAQ, you can click to learn more about the CompTIA ISAO or contact us at [email protected] for additional information. Or, if you want to read more about how joining the CompTIA ISAO can benefit your tech firm, visit CompTIA ISAO 101.
ISAO Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an ISAO?
An Information Sharing and Analysis Organization (ISAO) is a trusted community that actively collaborates to identify and disseminate information about cybersecurity threats. These organizations focus on providing technical information about attacks on businesses, governments and organizations. An ISAO gathers data about threat actors and their techniques from various sources. This data can come from governments, large and small companies, and cybersecurity organizations from around the world. The ISAO then crunches this data, turns it into useable information, and sends it to its members. Because an ISAO provides relevant, useful information, it effectively becomes a trusted advisor that raises an industry’s cybersecurity resilience.
An ISAO has many members, which can include individuals and organizations. These members join because they want to obtain important cybersecurity alerts. Members also share information with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, often in forums and groups.
An ISAO makes it possible to provide high-quality, critical cybersecurity intelligence to businesses of all types and in all industry sectors. When it comes to the managed service provider (MSP) community, for example, an ISAO can help identify ways to protect MSPs and their customers’ businesses. An ISAO allows organizations to share threat intelligence information and best practices as well as ask questions within a trusted community in order to raise the collective awareness and collaborate on proactive measures that can help minimize risk.
2. How are ISAOs different from ISACs?
Information Sharing and Analysis Center (ISAC) organizations existed for decades before the first ISAO was created. An ISAC is a non-profit organization that shares information between the public and private sector, much like an ISAO. But an ISAC focuses strictly on a particular industry sector focused on defined areas of “critical infrastructure.” For example, there are ISACs for critical infrastructure in the automotive industry, retailers, aviation, healthcare, and even the IT industry.
That’s where an ISAO comes in. An ISAO gathers, disseminates and documents cyber threat intelligence—much like an ISAC—but an ISAO does this across communities of interest or membership organizations like CompTIA.
3. Why are ISAOs more important than ever?
The onslaught of cybersecurity attacks has posed an existential threat to everyone—not just a single business sector. Ransomware reached critical levels some time ago, and even though the number of attacks has recently lowered, successful attacks remain a major issue. What’s more, intruders are able to stealthily infiltrate company networks to steal and alter information. These stealthy attacks, known as Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), have increased the need for companies of all kinds to share information. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have also increased across all businesses.
As cyber threats have increased, more organizations need access to the latest threat intelligence. Business leaders and cybersecurity professionals of all sectors have recognized the need to communicate more efficiently. In addition, in 2015, the Obama Administration issued Executive Order 13691 to promote the sharing of cybersecurity information security in the private sector. Putting aside competitive concerns, businesses collaborated to form ISAOs and now work together for the safety of their specific industry and the global economy.
4. What is threat intelligence?
Cyber threat intelligence is information that helps organizations identify the techniques attackers use to compromise security. Organizations collect data that spells out exactly how threat actors behave. For example, an MSP might have captured information about how a threat actor successfully attacked a particular vulnerability in a database server. In the spirit of information sharing, this company might want to inform the larger community about this problem, with suggestions on how to respond to or resolve it.
ISAOs vet and then share these insights about various types of attacks and hacker techniques. Threat intelligence includes technical information about evidence left behind by successful attackers. For example, threat intelligence can explain how an attacker can exploit a particular misconfiguration of a database server and obtain improper access to critical information. A threat feed can also explain how an attacker can exploit IoT devices or find ways to lurk mostly undetected in a network.
5. Why is threat intelligence important?
Threat intelligence can provide timely information that helps organizations better position security controls and manage risk. Too often, organizations spend time and money deploying security solutions and resources in the wrong places. Instead of “boiling the ocean,” or engaging in “defense in depth,” an organization that properly uses threat intelligence can build a strong defense with fewer resources to protect against threat actors. In other words, using threat intelligence correctly can allow businesses to work smarter, not harder, when it comes to their cybersecurity approach. Information and analysis of the latest cyber threats pose formidable protection for all businesses. The alternative can be costly.
Consider these recent statistics:
- Ransomware payments increased 33% in the first quarter of 2020.
- Businesses lost $9.3 billion in downtime and costs due to ransomware in the first quarter of 2020.
- 68% of business leaders have seen an increase in cyber risks in 2020.
6. What is a threat feed?
Remember, an ISAO collects data, turns it into relevant information, and shares it with its members. To get this information, an ISAO first obtains raw data from various resources, which might include:
- Threat feeds, such as those from Sophos Labs, Dark Cubed, and IT-ISAC, as well as the Spamhaus Project, the U.S.
Department of
Homeland Security (DHS) Automated Indicator Sharing (AIS) service and Cyber Information
Sharing and Collaboration Program (CISCP), the FBI’s Infragard Portal, and the United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre’s threat intel initiative, called the Cyber Security Information Sharing Partnership (CISP). These feeds contain raw data about current attacks. - Various Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) resources, such as information from social media, public news resources, newsletters, code repositories and the Dark Web.
- Information (including threat feeds) from ISACs.
- Other ISAOs.
- Trusted individual subject matter experts. For example, an ISAO can gather information from security specialists who work for organizations that are either partners or clients of the ISAO.
While many free data feeds exist, raw data feeds are only a part of what makes an ISAO valuable. An ISAO also leverages subject matter experts to organize and contextualize raw data, so it becomes useful, relevant information allowing ISAO members to make more informed decisions about their business’ cybersecurity.
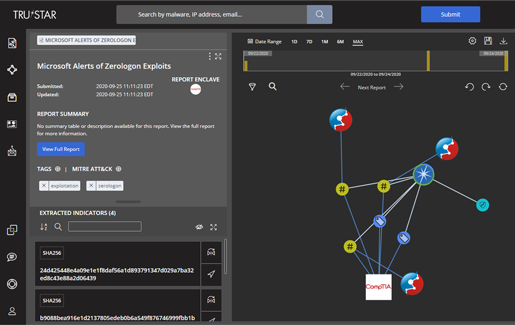
Example of a threat feed.
7. What does information from an ISAO look like?
An ISAO member receives information via various means, including email. Typically, members can then log in to the ISAO’s web interface to gain detailed information in a forum. Specific items of threat intelligence information can include:
- Alerts, including targeted notifications based on members technical and business profiles.
- Information about significant trends.
- Research from members or other industry sources.
When an organization joins an ISAO, the member first creates a detailed profile. This profile contains information about the technology used by the organization. This profile is important, because an ISAO creates alerts based on priorities important to the particular ISAO audience. Once the ISAO has an accurate profile of the member organization, the ISAO can then send more relevant information.
It is part of an ISAO’s job to then take the threat feed information and correlate it to the profiles of each ISAO member. This activity allows the ISAO to send relevant, targeted alerts to each member. These alerts can, for example, be based on the particular technology stack that each member uses or supports. For example, if you belong to an organization that uses predominantly a hybrid of Microsoft and Azure resources, then you would receive reports relevant to that particular approach. Someone who uses mostly AWS or Linux systems would receive different information and alerts.
But an ISAO doesn’t just focus only on technical information. An ISAO also gathers information about the member organization’s role in an industry sector, its strategic goals, and other information that attackers use when targeting a victim. The ISAO can then send relevant alerts to an organization if it fits the profile of recently attacked business sectors. As long as the member provides key information, cybersecurity alerts will help create a clear narrative that outlines how an organization can improve its security.
Each threat intelligence alert will include detailed information about a particular attack that exists “in the wild.” An ISAO alert will, for example, describe the tactic, technique, and procedure (TTP) used to conduct an attack and compromise a company. Each alert could contain detailed information about the attacker’s apparent tactical goal, as well as exactly how the attacker achieved that goal.
8. How do companies leverage information from an ISAO?
Member organizations can use ISAO threat reports to:
- Improve an organization’s overall cybersecurity situational awareness.
- Adjust resources as necessary.
- Inform both technical and non-technical stakeholders in an organization about strategic cybersecurity steps.
- Develop training, tests, and processes to ensure employee compliance regarding governance, risk and compliance and address risk management and liability.
9. What types of job roles do I need at my company to effectively understand, use, and provide threat intelligence?
One of the key goals of an ISAO is to make threat intelligence reports consumable by both technical and non-technical individuals. A knowledgeable IT professional will be able to use and interpret even the most technical reports from an ISAO—this person does not necessarily need to be a threat analyst or CISO. Small-to-medium businesses and similar organizations will likely have someone who wears multiple hats, including the role of a CISO, threat analyst or systems administrator. ISAO reports are designed to help these individuals too.
For IT professionals, the certifications along the CompTIA Cybersecurity Career Pathway validate skills that can be helpful when utilizing threat intelligence and other resources from an ISAO.
10. How can an ISAO contribute to a strong cybersecurity posture?
Information shared among members helps minimize risks to all companies in the industry. An ISAO helps improve cross-sector, peer-based communication. This can help certain sectors and business types that are increasingly under attack.
One of the major benefits of ISAO membership is that it can help all stakeholders in an organization communicate with each other better, as well as with other organizations. Attackers thrive in companies that have well-defined information silos, even if those silos are informal or undiscovered. This is especially the case if IT workers and employees are not properly working with management concerning cybersecurity.
ISAOs and the IT Industry
1. Why should managed service providers (MSPs) and tech vendors care about ISAOs?
In some ways, the better question here is, “Why are tech companies at risk?” MSPs have increasingly been targeted by attackers who use ransomware, various forms of malware, and Advanced Persistent Threat (ATP) attack methods.
One of the reasons MSPs have become a target is because they can act as a gateway for hackers to attack multiple organizations more easily. Many MSPs work with organizations that have ties and contracts with governments and large businesses. If one MSP or one MSP client is compromised, an attacker can use this compromise to potentially attack many more companies along a supply chain.
Consider the following statistics:
- 83% of MSPs report having customer cyberattacks (Continuum).
- 74% of MSPs report being cyber victim themselves (Continuum).
- Organizations expect to spend $170 billion on cybersecurity by 2022 (Gartner).
Organizations worldwide—and their partners—are now required to comply with privacy laws and security frameworks. These can include laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), among many others. Belonging to an ISAO will help organizations remain compliant, as they will be more situationally aware of issues that can lead to security and privacy issues. An improved security posture may help eliminate potential legal liability you may face in the event of a breach.
2. Will my customers care that I’m an ISAO member?
Businesses of all sizes want partners they can trust that can protect them and their data. As an MSP, ISAO membership can demonstrate your commitment to due diligence and commitment to protecting customers. Meanwhile, ISAO membership can also increase a tech vendor’s reputation as a trusted partner with both channel partners and customers. Membership in the CompTIA ISAO, a global, industry-wide network solely focused on cybersecurity, should increase trust and loyalty with your customers. The information you receive can help you create services and adopt a posture that may give you a key differentiator to your customers and partners.
3. What is the CompTIA ISAO?
The CompTIA ISAO is a member-based network of security and business professionals dedicated to providing critical threat intelligence, actionable insight, and analysis to technology vendors, MSPs, solution providers, integrators, distributors, business technology consultants, and their customers.
Currently, the CompTIA ISAO has more than 700 members. CompTIA has partnered with the IT-ISAC, TruSTAR, Sophos, DHS, and other organizations to obtain their threat feeds, providing the organization with a comprehensive library of available data to analyze. The CompTIA ISAO is a vendor-neutral, member-led community. Members also can use the Cyber Forum where they can collaborate with one another, share best practices, and access the threat intelligence reports. Through our TruSTAR Enclave membership, members of the CompTIA ISAO can search through these data feeds as they wish. An added member benefit is a dedicated, private Enclave for the members business.
Want more Q&A about the CompTIA ISAO? Read CompTIA ISAO 101: What Is it, Why Does it Matter, and How Can You Benefit?
Learn more about joining the CompTIA ISAO.

CompTIA offers several membership categories, each with a wealth of resources to help protect your tech business and its customers. Learn more about the CompTIA ISAO and corporate membership. CompTIA is also actively recruiting industry leaders to serve as partners and advisors to the ISAO. Contact [email protected] for more information about membership or partnership opportunities.
Read more about Cybersecurity.

